A single ransomware attack can halt a manufacturing production line for days, costing hundreds of thousands of dollars while competitors continue shipping. The challenge isn’t just stopping attackers—it’s doing so without creating the very downtime you’re trying to prevent.
This guide covers the layered security strategies that protect manufacturing networks in 2026, from IT/OT segmentation and Zero Trust implementation to automated patching and continuous monitoring, all designed to keep production running while keeping threats out.

Building a secure manufacturing network without downtime starts with a layered defense strategyBuilding a secure manufacturing network without downtime starts with a layered defense strategy. This means integrating Zero Trust Architecture, segmenting IT and OT networks with industrial firewalls, deploying ruggedized hardware, automating patch management, implementing multi-factor authentication, and maintaining continuous monitoring. The goal is balancing strict security controls with the operational reality that production lines cannot stop.
Manufacturing environments differ fundamentally from traditional office networks. Your production floor runs around the clock, and taking systems offline for security updates can cost thousands of dollars per minute in lost output. Meanwhile, operational technology—the systems controlling physical machinery like PLCs, sensors, and robotics—often runs on legacy equipment that was never designed with cybersecurity in mind.
This convergence of IT and OT creates distinct challenges:
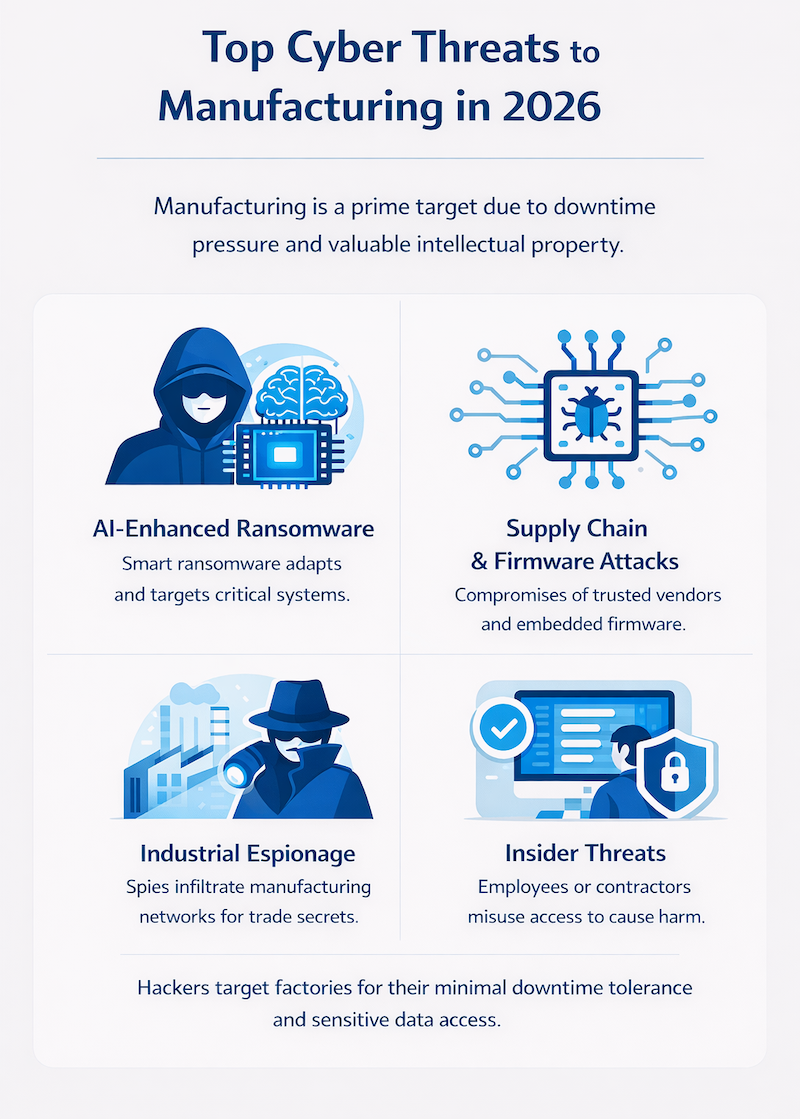
Manufacturing has become a prime target for attackers because downtime creates immediate pressure to pay ransoms or restore access quickly. Knowing what you’re defending against helps prioritize security investments.
Modern ransomware uses artificial intelligence to evade detection and identify the most critical systems to encrypt, requiring advanced threat detection capabilities to counter these evolving attacks. Attackers have shifted from simply stealing data to disrupting operations entirely. They know a manufacturer will pay faster when production lines stop moving.
Attackers increasingly infiltrate through trusted vendors and software updates. Firmware—the low-level software embedded in hardware devices—provides an especially attractive target because it’s rarely monitored and can survive system reinstalls.
IoT sensors and programmable logic controllers create entry points that traditional security tools often miss. PLCs are specialized computers that control manufacturing processes, and compromising them gives attackers both operational control and access to proprietary production data.
Not all threats come from outside your organization. Employees, contractors, and compromised remote access tools represent significant risk vectors. A single set of stolen credentials can provide attackers with legitimate-looking access to critical systems.
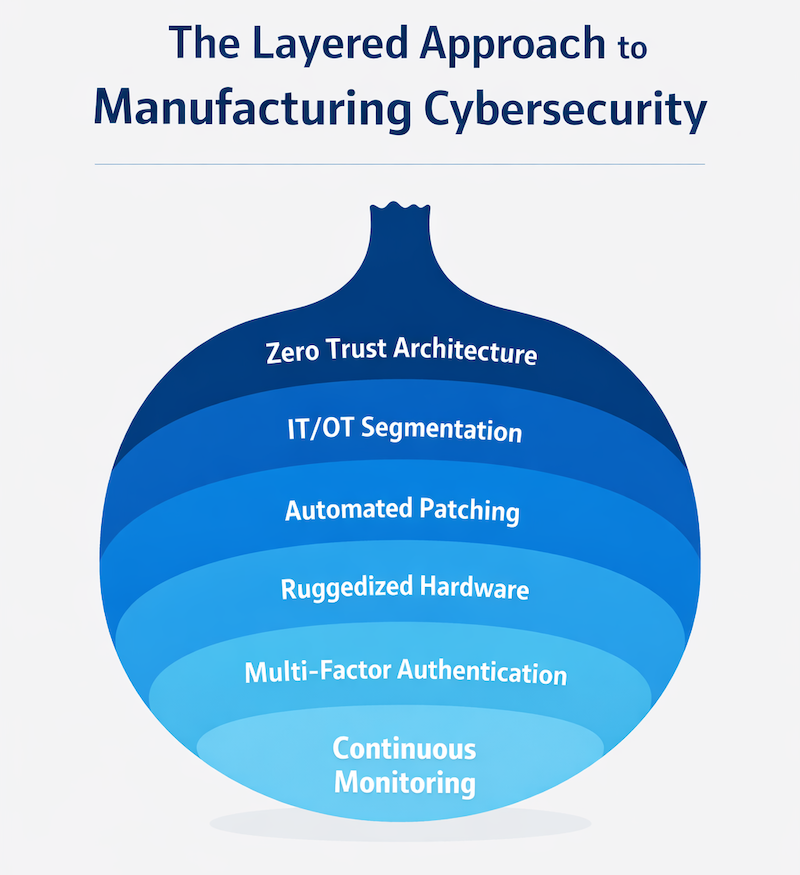
Firewalls alone cannot protect modern manufacturing environments. The old model of building a strong wall around your network assumes threats stay outside, but today’s attacks often originate from within or bypass perimeter defenses entirely.
Security tools designed for corporate IT environments don’t understand OT protocols or the unique traffic patterns of industrial systems. They generate false positives that disrupt operations or miss genuine threats hiding in legitimate-looking industrial communications.
When IT and OT monitoring systems don’t communicate, attackers exploit the blind spots between them. An intrusion might appear normal to each system individually while the combined pattern reveals malicious activity.
Waiting until after an attack to respond means accepting significant downtime. Proactive prevention—detecting and stopping threats before they impact production—costs far less than incident response and recovery.
Network segmentation divides your infrastructure into isolated zones, limiting how far an attacker can move after gaining initial access. This approach protects production systems even when other parts of the network are compromised.
Creating boundaries between corporate systems and production floor systems prevents an email phishing attack from reaching your PLCs. You’ll still want controlled data flow for analytics and monitoring, though. The goal is managed access, not complete isolation.
Micro-segmentation takes isolation further by protecting individual machines or processes. If an attacker compromises one production cell, they cannot move laterally to others without triggering additional security controls.
Effective segmentation stops attackers from moving through your network while allowing legitimate production communication. This requires mapping your operational workflows before implementing controls.
| Segmentation Type | Best For | Production Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Network-level | IT/OT separation | Minimal when planned |
| Micro-segmentation | Critical assets | Requires careful configuration |
| Application-level | Data flow control | Ongoing monitoring needed |
Zero Trust architecture operates on a simple principle: never trust, always verify. Every user, device, and connection is authenticated and authorized before accessing resources, regardless of whether they’re inside or outside your network perimeter.
Continuous authentication means credentials are validated not just at login, but throughout each session, while tracking all devices accessing your network. Multi-factor authentication adds additional verification layers that prevent stolen passwords from granting access.
Least privilege means users and systems receive only the minimum access rights required for their specific functions. An operator who monitors production metrics doesn’t require the ability to modify PLC programming.
Implementing Zero Trust doesn’t require a complete network overhaul. Start with your highest-risk systems, test thoroughly in isolated environments, and expand gradually. This phased approach maintains production continuity while steadily improving security posture.
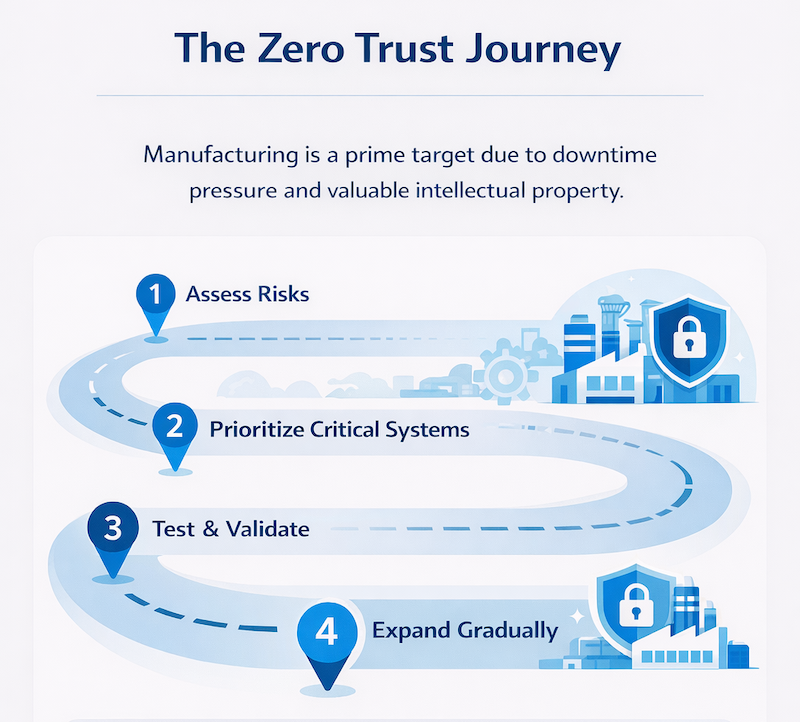
Patching closes security vulnerabilities, yet manufacturing systems often run months or years behind on updates because taking them offline disrupts production. Automation bridges this gap by applying updates efficiently during planned windows.
Align security updates with existing maintenance schedules. Most manufacturing facilities already have planned downtime for equipment servicing, and these windows provide opportunities for security updates without additional production impact.
Before deploying patches to production systems, validate them in staging environments that mirror your operational setup. This catches compatibility issues before they cause unexpected downtime.
Autonomous Endpoint Management automates the patching process while maintaining human oversight for rollbacks. AEM systems can apply updates during brief operational pauses, reducing the vulnerability window without requiring extended downtime.
Redundancy ensures production continues even during security incidents or system failures, forming a critical component of disaster recovery planning. Failover—the automatic switching to backup systems when primary systems fail, eliminates single points of failure that attackers can exploit.
Multiple network paths ensure communication continues if one path is compromised or fails. Critical production systems benefit from redundant connections that automatically route around problems.
Automated failover removes human delay from the recovery process. When systems detect a failure, backup resources activate immediately without waiting for manual intervention.
Visibility across both IT and OT environments enables threat detection before attacks cause downtime. You cannot protect what you cannot see, and manufacturing environments often have significant blind spots between corporate and production networks.
A Security Operations Center provides round-the-clock monitoring by trained analysts who can distinguish genuine threats from false alarms. This continuous oversight catches attacks that automated systems might miss.
Monitoring industrial control systems requires specialized network management tools that understand OT protocols without impacting system performance. Generic IT monitoring tools often generate excessive false positives in manufacturing settings, so purpose-built solutions provide better results.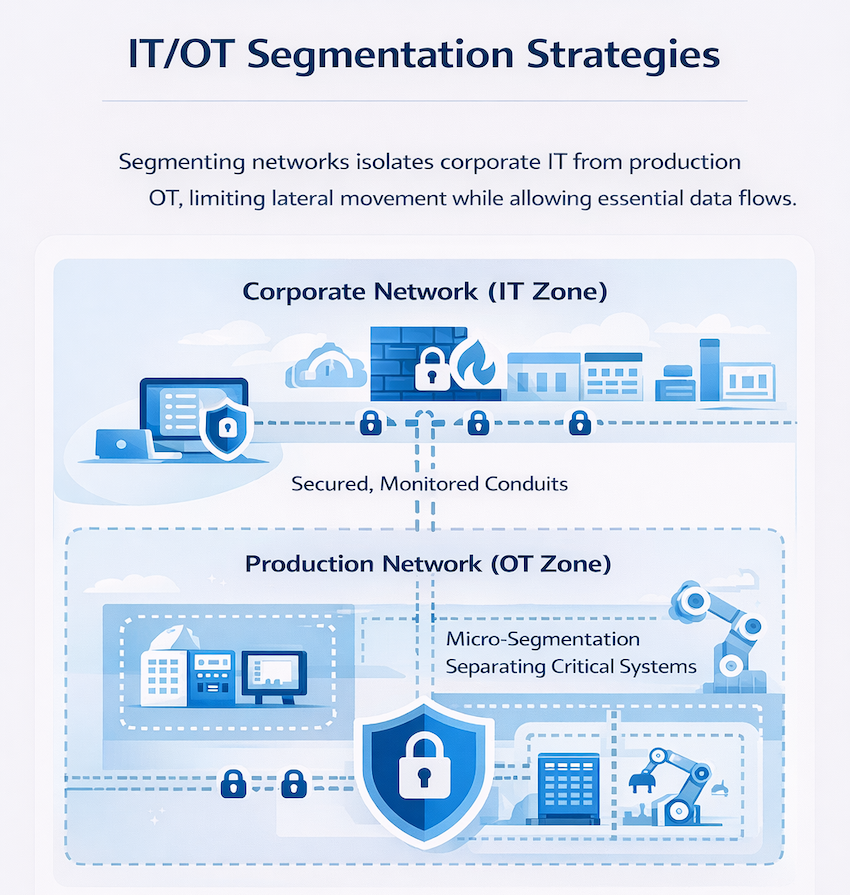
Following established frameworks ensures comprehensive security coverage and supports compliance requirements. NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) and CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) provide guidance specifically relevant to manufacturing.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework organizes security activities into five functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Mapping your security program to this framework reveals gaps and provides a roadmap for improvement.
CISA publishes specific guidance for industrial environments that addresses the unique challenges of OT security. The recommendations reflect real-world attack patterns and proven defensive strategies for manufacturing operations.
Vendors and partners create security risks that extend beyond your direct control. Managing vendor relationships requires balancing necessary business collaboration with appropriate security controls.
Evaluate third-party security practices before granting access to your systems. Ongoing monitoring ensures vendors maintain acceptable security standards throughout your relationship.
Provide necessary access while limiting risk exposure through segmented connections, time-limited credentials, and session monitoring. Contractors receive access only to specific systems required for their work, and credentials expire after project completion.
Manufacturing security requires expertise in both IT and OT environments—a combination that’s difficult to build internally. IT GOAT provides U.S.-based SOC and NOC teams with experience protecting production environments, delivering proactive monitoring and rapid response without disrupting operations.
Our approach emphasizes prevention over reaction, strategic guidance through dedicated vCIO leadership, and responsive support that manufacturing operations demand.
Book an Appointment to discuss how we can help secure your manufacturing network without impacting production.
Implementation timelines vary based on network complexity and existing infrastructure. Most manufacturers benefit from a phased rollout spanning three to twelve months, starting with highest-risk systems and expanding gradually to minimize production disruption.
Start with systems that directly control production processes and systems connected to external networks. Production control systems and internet-facing assets represent the highest risk for both downtime and unauthorized access.
Implement segmented access that limits vendors to only the specific systems they require, combined with multi-factor authentication and session monitoring. Time-limited credentials that expire after project completion further reduce ongoing risk exposure.
See the power of IT GOAT.
The world’s most advanced cybersecurity platform catered specifically to your business’ needs.
Keep up to date with our digest of trends & articles.
By subscribing, I agree to the use of my personal data in accordance with IT GOAT Privacy Policy. IT GOAT will not sell, trade, lease, or rent your personal data to third parties.

Mitigate All Types of Cyber Threats
Experience the full capabilities of our advanced cybersecurity platform through a scheduled demonstration. Discover how it can effectively protect your organization from cyber threats.

IT GOAT: Threat Intel & Cyber Analysis
We are experts in the field of cybersecurity, specializing in the identification and mitigation of advanced persistent threats, malware, and exploit development across all platforms.

Protect Your Business & Operations
Exceptional performance in the latest evaluations, achieving 100% prevention rate and providing comprehensive analytic coverage, unmatched visibility, and near-instant detection of threats.
We use cookies to enhance site performance and user experience. Your data stays private — we don’t sell your information or share it with unrelated third parties. To find out more about the cookies we use, view our Privacy Policy.