Moving to Office 365 sounds straightforward until you’re three days into a migration that was supposed to take one, watching helpdesk tickets pile up while employees can’t access their calendars. The technical complexity alone—legacy system conflicts, permission mismatches, Microsoft’s own throttling limits—catches most organizations off guard.
This guide walks through the most common Office 365 migration pain points, from data loss risks to user adoption struggles, along with a practical checklist and best practices to help your transition go smoothly.

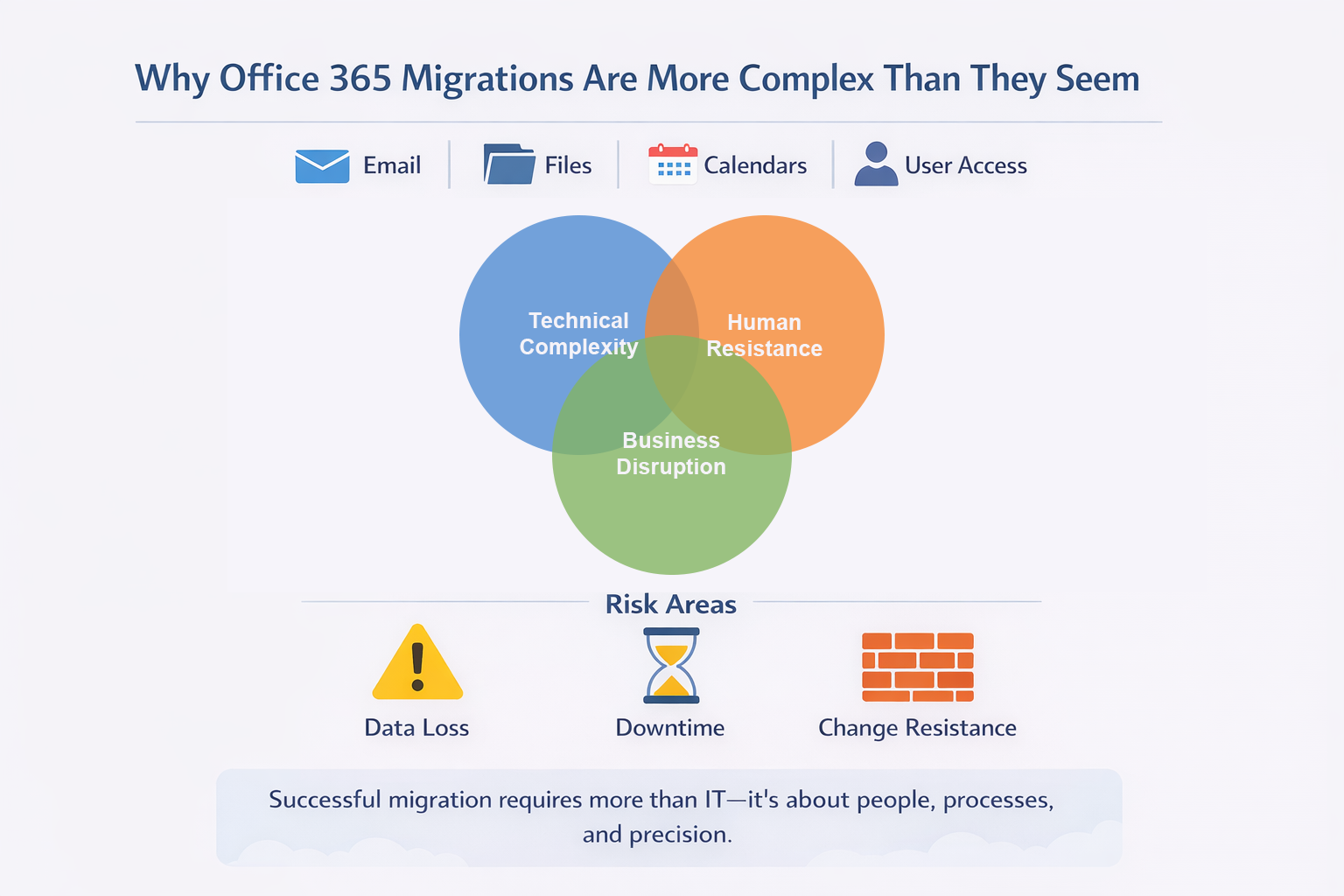
Office 365 migrations involve moving email, files, calendars, and collaboration tools from one system to Microsoft’s cloud platform. The process combines technical complexity, business disruption risks, and human factors that make it far more difficult than copying files between folders. Organizations typically underestimate the scope because they’re dealing with intricate Exchange and SharePoint environments, legacy permission models, and the real possibility of data loss or security gaps.
A migration touches nearly every part of how your team works. Years of business-critical data transfer while access controls stay intact, metadata remains preserved, and operations keep running. Meanwhile, employees accustomed to existing workflows may resist change, and even brief disruptions to email or calendar access ripple through productivity.
Pain Point: Older systems rarely integrate smoothly with modern cloud platforms.
Legacy systems—aging on-premises servers, outdated Exchange versions, or custom applications built years ago—often use different permission structures, file formats, or authentication methods than Office 365 expects. This mismatch creates friction at every step. Linked files break, custom workflows stop functioning, and data that looked fine in the old system may not transfer correctly.
Pain Point: Even well-planned migrations can interrupt daily operations.
Email access, calendar synchronization, and shared document collaboration may experience gaps during the transition period. For most organizations, even a few hours without email feels significant. Missed communications, delayed customer responses, and stalled internal processes all carry real costs that extend beyond simple inconvenience.
Pain Point: Data can be lost, corrupted, or incompletely transferred during migration.
Emails may arrive without attachments, files may lose their metadata, and entire folders can fail to transfer without obvious warning signs. Often, problems don’t surface until weeks later when someone searches for a critical document or email thread that no longer exists in the new environment.
Pain Point: Most organizations accumulate massive amounts of ROT data—redundant, outdated, and trivial information that serves no business purpose.
Migrating unnecessary data wastes time, increases costs, and clutters your new Office 365 environment from day one. That archive of emails from 2012 and the duplicate files scattered across shared drives all add to migration volume without adding value.

Pain Point: Insufficient internet bandwidth can slow migrations dramatically or cause them to fail entirely.
Organizations with large mailboxes, extensive file libraries, or limited network infrastructure often find migrations taking far longer than projected. This becomes especially problematic when trying to minimize downtime and complete the migration within a specific maintenance window.
Pain Point: Running both on-premises and cloud systems simultaneously introduces significant complexity.
A hybrid environment—where some users remain on old systems while others move to Office 365—requires careful configuration to maintain email flow, calendar sharing, and consistent user experiences across both platforms. Many organizations require this coexistence period, yet it remains one of the most technically demanding aspects to configure correctly.
Pain Point: Microsoft intentionally limits how fast data can be migrated to protect overall service performance.
Throttling means your migration may proceed more slowly than your network capacity would otherwise allow. A migration expected to complete over a weekend might actually require several weeks of incremental data transfers.
Pain Point: Technology changes only succeed when people embrace them.
Employees unfamiliar with Office 365’s interface, frustrated by workflow changes, or simply resistant to learning new tools can undermine even technically flawless migrations. Productivity typically dips during the transition period as users adjust to new ways of working.
Pain Point: Rushing into migration without thorough assessment leads to preventable failures.
Organizations that skip the discovery phase, underestimate data volumes, or set aggressive deadlines often find themselves scrambling to recover from avoidable problems.
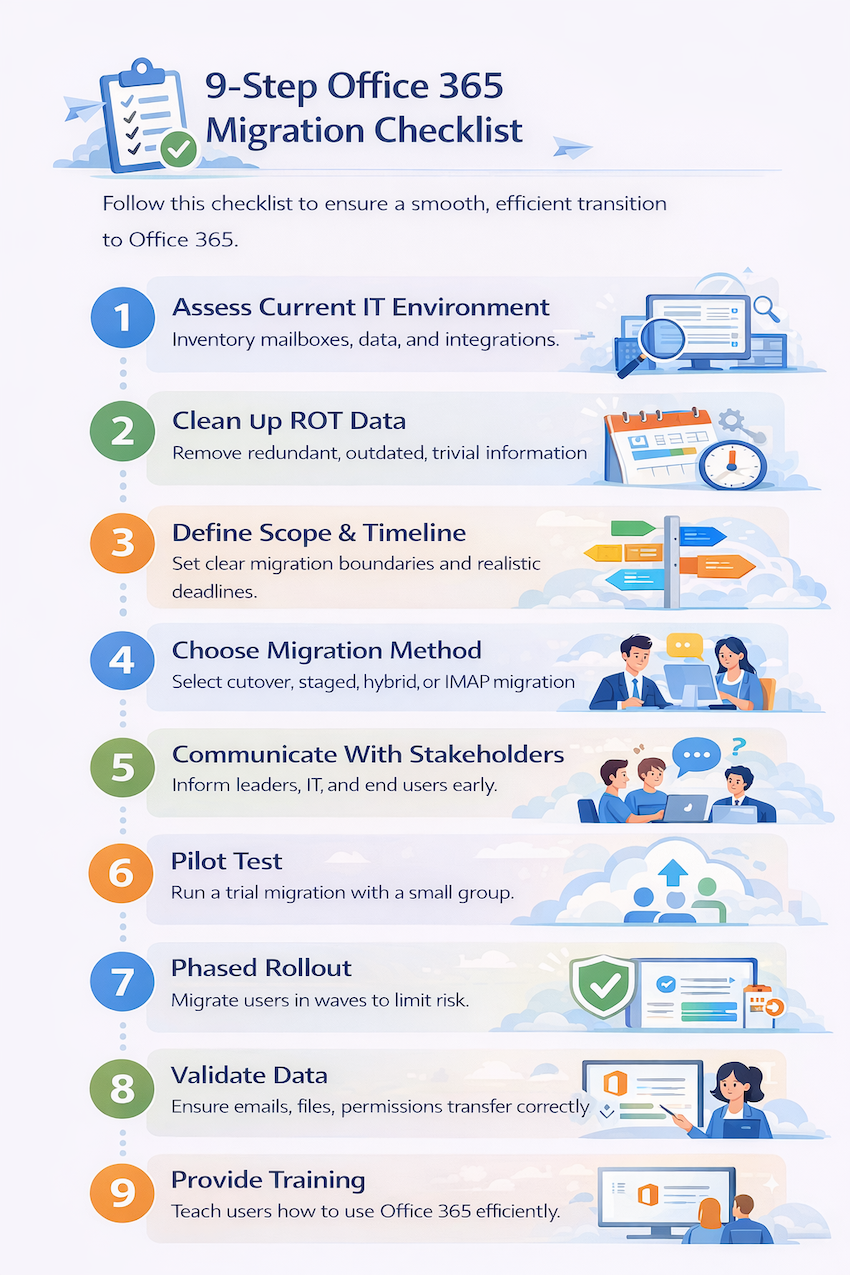
A structured approach dramatically improves your chances of a smooth transition.
Inventory everything before beginning—mailbox counts, data volumes, applications, integrations, and dependencies. Effective planning requires knowing exactly what you’re working with.
Remove ROT data before migration. This reduces the volume being transferred, speeds up the process, and provides a cleaner starting point in Office 365.
Establish clear boundaries for what’s being migrated and when. Realistic deadlines account for testing, potential issues, and the learning curve your team will experience.
Different scenarios call for different approaches:
Inform leadership, IT staff, and end users about timelines, expected disruptions, and what they’ll do differently. Surprises breed frustration.
Test with a small group before full rollout. Pilot testing reveals issues while they’re still manageable and builds confidence in your process.
Migrate in waves rather than all at once. Phased approaches limit risk, allow troubleshooting between phases, and prevent organization-wide disruption if problems arise.
Verify that emails, files, and permissions transferred correctly. Spot-checking isn’t enough—systematic validation catches issues before users discover them.
Ensure users know how to navigate Office 365 and have access to help resources. The migration isn’t complete until people can work effectively in the new environment.
Beyond the checklist, strategic practices help organizations avoid common pitfalls.
Audit your infrastructure thoroughly before any migration activity begins. Document dependencies, identify potential conflicts, and understand your current state completely.
Minimize business disruption by migrating during evenings, weekends, or periods of low activity. Off-peak scheduling provides buffer time for troubleshooting without impacting normal operations.
For larger organizations, running both environments simultaneously during transition often makes sense. Hybrid coexistence allows gradual migration while maintaining business continuity, particularly with co-managed IT approaches.
Use monitoring tools to track status, catch errors early, and adjust your approach as circumstances change. Visibility into the process helps you respond quickly when issues arise.
Maintain detailed records throughout the migration. Documentation proves valuable for regulatory requirements, future reference, and troubleshooting if questions arise later.
Migrations create temporary vulnerabilities that require attention.
Data moving between systems can be vulnerable without proper encryption and secure connections. Encrypted transfers protect sensitive information during this transitional period.
Permissions may not transfer correctly between systems, potentially leaving data exposed to unauthorized users or inaccessible to those who require it. Careful mapping and validation of access controls prevents gaps.
Migrations can temporarily break compliance with frameworks like HIPAA, SOC 2Migrations can temporarily break compliance with frameworks like HIPAA, SOC 2, or industry-specific regulations. Planning for compliance continuity throughout the migration protects your organization from audit failures.
Attackers often exploit migration confusion to target employees with fake login requests or credential harvesting attempts. User awareness becomes especially important during this period.
Email typically represents the most critical and complex component of Office 365 migrations.
Large mailboxes slow migration significantly and may hit Microsoft’s transfer limits. Pre-migration cleanup and realistic timeline planning help manage mailbox constraints.
Calendar entries, recurring meetings, and contact lists don’t always transfer cleanly. Testing calendar and contact elements specifically during pilot migrations helps identify issues early.
PST files—local Outlook data files many users have accumulated over years—present particular challenges. PST files are often scattered across individual workstations and may contain data that doesn’t exist anywhere else.
Group memberships, shared mailboxes, and send-as permissions frequently require manual reconfiguration. Distribution lists and permissions rarely migrate automatically without issues.
Choosing between self-service tools and professional assistance depends on your organization’s specific situation.
| Factor | DIY Migration Tools | Managed IT Support |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | Small, simple environments | Complex or multi-location organizations |
| Cost | Lower upfront investment | Higher but includes expertise |
| Risk level | Higher without experience | Lower with professional oversight |
| Time commitment | Significant internal effort | Minimal internal burden |
| Support availability | Limited to vendor documentation | Dedicated team throughout process |
For small teams with straightforward setups—perhaps under 50 users with standard email and file storage—native Microsoft tools or third-party migration software can work well. DIY approaches require internal IT expertise and available time to manage the process.
Larger organizations, those with compliance requirements, or businesses with complex hybrid environments typically benefit from expert assistance. The cost of professional support often proves less than the cost of extended downtime or failed migration attempts.

Selecting a qualified migration partner significantly impacts your project’s success.
IT GOAT approaches Office 365 migrations with proactive planning, security-first methodology, and dedicated support throughout the process. Our U.S.-based team handles the technical complexity so you can focus on running your business, and we remain available for training and support long after the migration completes.
Ready to discuss your Office 365 migration? Book a consultation to explore how we can help your organization transition smoothly.
Migration timelines vary based on organization size, data volume, and complexity. Small businesses might complete migration in a few days, while enterprises with hybrid environments may require several months of phased work.
Yes, with proper planning, pilot testing, and validation steps, organizations can achieve zero data loss. The key lies in thorough preparation and systematic verification after each migration phase.
Having a rollback plan in place before starting proves essential. If failure occurs, work with your IT team or partner to diagnose the specific failure point before attempting to resume the migration.
Costs depend on the migration method, organization size, and whether you use internal resources or hire external support. DIY approaches have minimal direct costs but require significant time investment, while fully managed migrations involve higher fees but include expertise and reduced risk.
No, phased migrations allow organizations to move users and data in batches. Phased approaches reduce risk, allow troubleshooting between waves, and maintain business continuity throughout the transition.
See the power of IT GOAT.
The world’s most advanced cybersecurity platform catered specifically to your business’ needs.
Keep up to date with our digest of trends & articles.
By subscribing, I agree to the use of my personal data in accordance with IT GOAT Privacy Policy. IT GOAT will not sell, trade, lease, or rent your personal data to third parties.

Mitigate All Types of Cyber Threats
Experience the full capabilities of our advanced cybersecurity platform through a scheduled demonstration. Discover how it can effectively protect your organization from cyber threats.

IT GOAT: Threat Intel & Cyber Analysis
We are experts in the field of cybersecurity, specializing in the identification and mitigation of advanced persistent threats, malware, and exploit development across all platforms.

Protect Your Business & Operations
Exceptional performance in the latest evaluations, achieving 100% prevention rate and providing comprehensive analytic coverage, unmatched visibility, and near-instant detection of threats.
We use cookies to enhance site performance and user experience. Your data stays private — we don’t sell your information or share it with unrelated third parties. To find out more about the cookies we use, view our Privacy Policy.